Iran is located in southwest Asia and in the Middle East region, which is called the intersection of the World. It is neighbor to Armenia, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan in the north It borders with Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Saudi Arabia through the Persian Gulf and the Oman Sea. On the west, Iran’s neighbors are Turkey and Iraq, and on the east it’ s neighbors are Afghanistan and Pakistan. In other words, Iran has sea and earth border with 15 countries. Iran is located in a crossing region as a bridge to connect European countries to Asia. Also, using Iran’s route to connect the East and West of the world has many economic advantages; Because it is cheaper than other routes, this can be attractive to Iran’s neighbors and other countries around the world.
History of transit in Iran
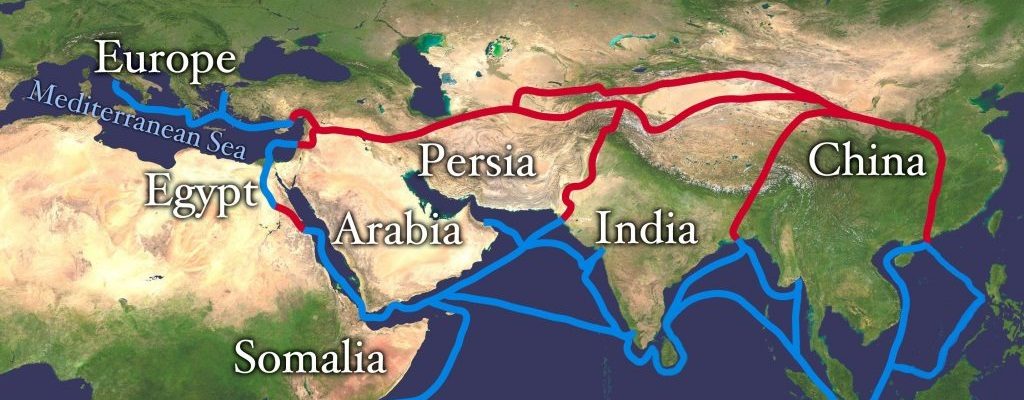
Of course, Iran’s role in connecting the West and the East of the world has a historical record, for example the Silk Road, which stretched from Eastern Europe to Eastern Asia, which much of it passed through northern parts of Iran. In recent years, some countries, such as China, are going to revive the road.
Transit system in Iran
Iran has 90 airports, 13 of which are international. The best airports in Iran are Imam Khomeini and Mehrabad International Airports, both of which are located in the Iranian capital, Tehran. . About 70 percent of Iran’s total flights are operated by these two airports. The price of gasoline in Iran is maximum 5 cents, which is the third-lowest cost in the world, so it has made many shipping services cheaper.
Iran’s freeways and highways length are over 20,000 kilometers. This country’s rail lines are longer than 11,000 kilometers. The number of road transport trucks in this country has reached more than 308,000.
There are currently 144 active small and large custom houses, 50 of which are border crossings. Communication with open water through the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea in southern Iran is a strategic necessity for many Central Asian landlocked countries. And the transportation of essential commodities through it and Iran’s communication routes is more cost-effective for Central Asia than air routes.
Iran has fourteen large active ports, each of which is considered to be a special economic zone. Most of Iran’s ports are important trading terminals that carry out much of the country’s import and export through these ports. The ports of Shahid Rajaee and Imam Khomeini carry the main burden of Iran’s trade with other countries.
Locating the strategic strait of Hormuz as the world’s international energy transit route, and securing it by Iran, the strategic port of Chabahar in the southeast as a gateway to open waters and favorable shipping routes on the northern margin of the Oman Sea are examples of Iran’s advantages in shipping. It is interesting to know that Iran is India’s only geopolitical access to Central Asia.
All the facts and figures mentioned above are proof of Iran’s extraordinary ability to play a role in international transit and shipping. Iran’s path to these cases can provide many benefits in reducing time or cost in international trade.
In Iran directory complex, we can provide transportation services through Iran from different points of entry and exit in the south, north, east and west of the country. If you need to know more about or use these services, please contact this complex through the Contact us page.
This post is also available in:  中文 (Chinese)
中文 (Chinese)